一、数组
JavaScript数组常用api
改变原数组:
push 末尾添加数据 返回length
pop 末尾删除数据 返回删除的那个数据
unshift 头部添加数据 length
shift 头部删除数据 删除的那个数据
reverse 翻转数组 返回翻转好的数据
sort 按照位排序 可以传入比较函数 返回排好的数组
splice 截取数组或者删除并插入数据 返回一个新数组里面为截取到的值
不改变原数组的方法
concat 合并数组 返回一个新的数组
join 数组转成字符串
slice 截取数组的一部分数据 返回截取到的数据
indexOf 从左检查数组中有没有这个数值 返回第一次出现的索引或者-1
lastIndexOf 从右检查数组中有没有这个数值
ES6新增的数组方法
forEach 遍历数组
map 映射数组
filter 过滤数组
every 判断数组是不是满足所有条件 以return的形式执行条件
some 数组中有没有满足条件的
find 获取数组中满足条件的第一个数据
reduce 叠加后的效果
二维数组
定义一个二维数组
let twod = [];
let rows = 5;
for (let i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
twod[i] = [];
}二维数组遍历 双重for,flat
二、栈
先进后出
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.dataStore = [];
}
push(element) {
this.dataStore[this.top++] = element;
}
peek() {
return this.dataStore[this.top - 1];
}
pop() {
return this.dataStore[--this.top];
}
clear() {
this.top = 0;
}
length() {
return this.top;
}
}三、队列
先进先出
代码实现:
class Queue {
enqueue(element) {
this.dataStore.push(element);
}
dequeue() {
return this.dataStore.shift();
}
front() {
return this.dataStore[0];
}
back() {
return this.dataStore[this.dataStore.length - 1];
}
toString() {
let retStr = "";
for (let i = 0; i < this.dataStore.length; ++i) {
retStr += this.dataStore[i] + "
";
}
return retStr;
}
empty() {
if (this.dataStore.length == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}四、链表
链表是由一组节点组成的集合。每个节点都使用一个对象的引用指向它的后继。指向另一个节点的引用叫做链。
数组:添加和删除比较慢,查找速度快 链表:查找速度慢,添加和删除速度慢
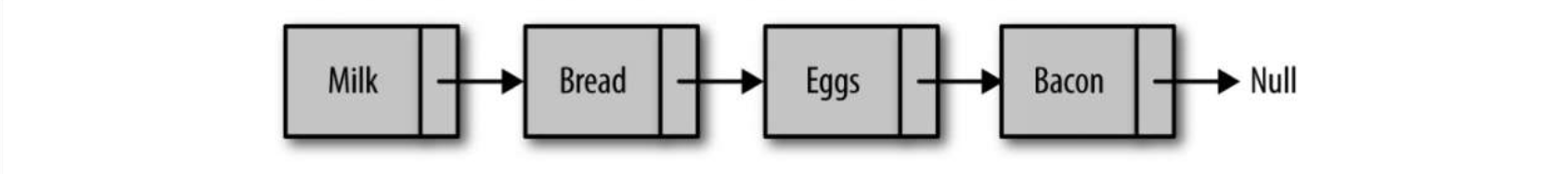
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LList {
constructor() {
this.head = new Node("head");
}
remove(item) {
let prevNode = this.findPrevious(item);
if (!(prevNode.next == null)) {
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
findPrevious(item) {
let currNode = this.head;
while (!(currNode.next == null) && currNode.next.element != item) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
display() {
let currNode = this.head;
while (!(currNode.next == null)) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
find(item) {
let currNode = this.head;
while (currNode.element != item) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
insert(newElement, item) {
let newNode = new Node(newElement);
let current = this.find(item);
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
}五、字典
字典是一种以键-值对形式存储数据的数据结构,就像电话号码簿里的名字和电话号码一样,和map类似。
class Dictionary {
constructor() {
this.datastore = new Array();
}
add(key, value) {
this.datastore[key] = value;
}
find(key) {
return this.datastore[key];
}
remove(key) {
delete this.datastore[key];
}
}六、散列表(哈希表)
散列表是基于数组进行设计的,所有元素根据和该元素对应的键,保存在数组的特定位置。使用散列表存储数据时,通过一个散列函数将键映射为一个数字,这个数字的范围是0到散列表的长度。下图以一个小型电话号码簿为例,阐释了散列的概念。
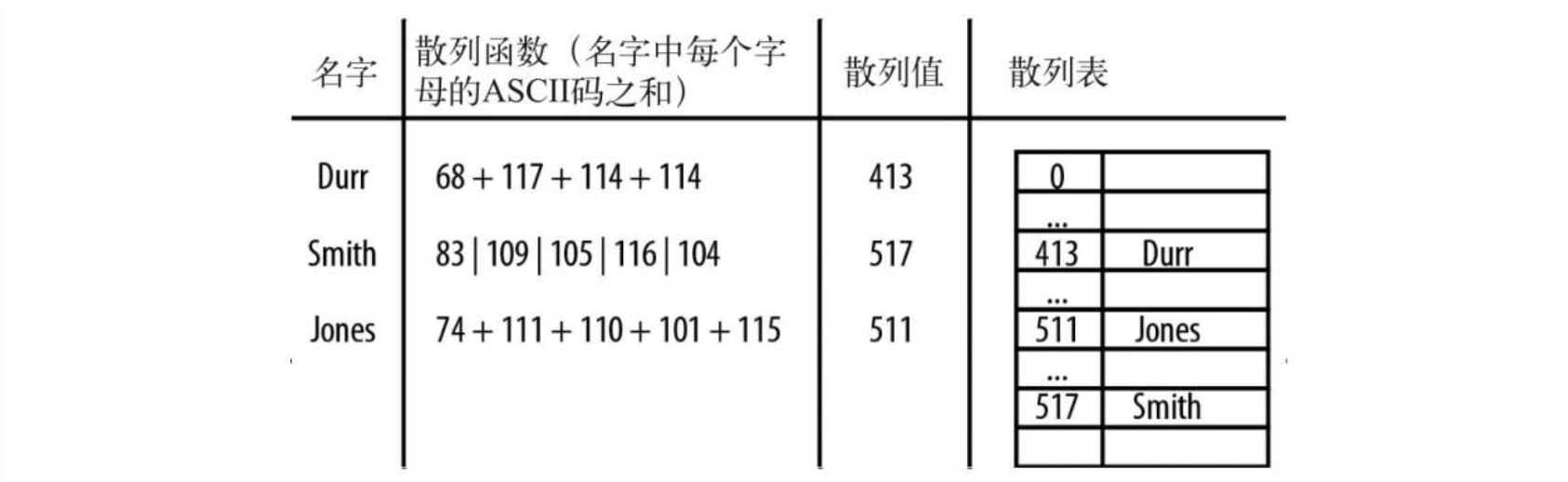
代码演示:
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.table = new Array(137);
}
// 散列函数的一个简单实现,假设输入的问英文字符串,可以用每个字符对应的ASCII码表示散列值
simpleHash(data) {
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
total += data.charCodeAt(i);
}
return total % this.table.length;
}
put(data) {
let pos = this.simpleHash(data);
this.table[pos] = data;
}
get(key) {
return this.table[this.simpleHash(key)];
}
showDistro() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
if (this.table[i] != undefined) {
console.log(this.table[i]);
}
}
}
}
const hs = new HashTable();
let names = ["sun", "lebron", "xiaoming"];
names.forEach((item) => {
const hsNum = hs.simpleHash(item);
hs.table[hsNum] = item;
});
hs.showDistro();当散列函数对于多个输入产生同样的输出时,就产生了碰撞。
七、集合
集合(set)是一种包含不同元素的数据结构。集合中的元素称为成员。集合的两个最重要特性是:首先,集合中的成员是无序的;其次,集合中不允许相同成员存在。
代码实现:
class Set {
constructor() {
this.dataStore = [];
}
add(data) {
if (this.dataStore.indexOf(data) < 0) {
this.dataStore.push(data);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
remove(data) {
let pos = this.dataStore.indexOf(data);
if (pos > -1) {
this.dataStore.splice(pos, 1);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
show() {
return this.dataStore;
}
}八、树
树是一种非线性的数据结构,以分层的方式存储数据。树被用来存储具有层级关系的数据,比如文件系统中的文件;
二叉树示例图: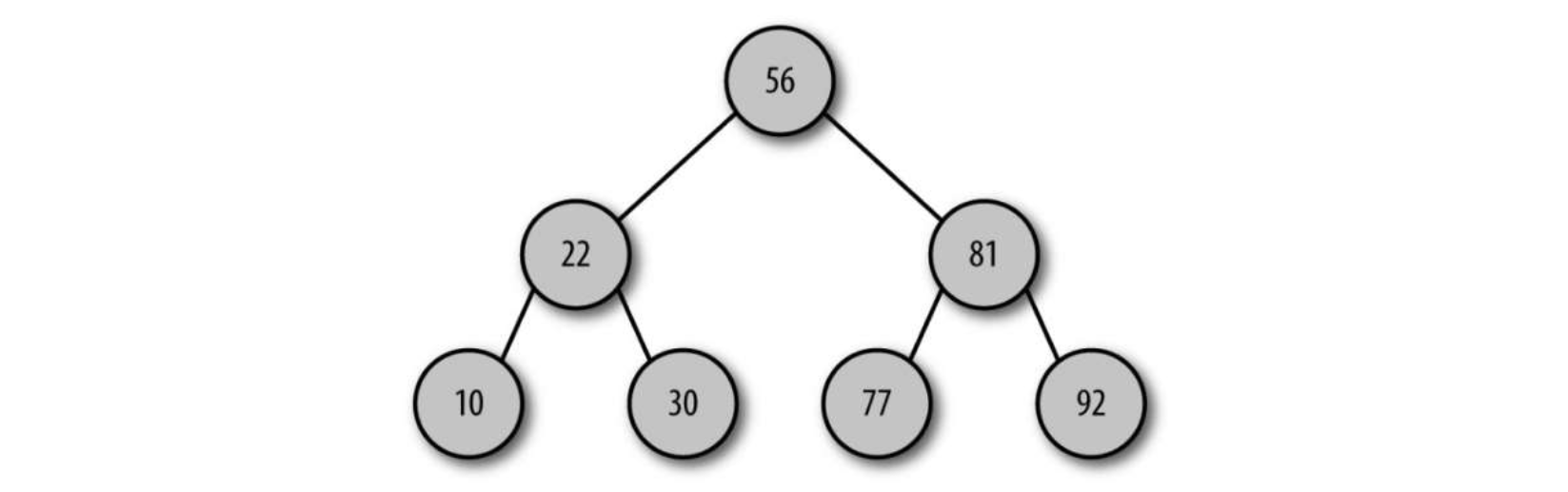
二叉树左序遍历:
let root = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: null,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: null,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
};
function foo(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const queue = [root];
const res = [];
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = queue.shift();
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
node.val != null && res.push(node.val);
}
}
return res;
}
console.log(foo(root));九、图
些许复杂,暂不谈论。
十、排序算法
十一、查找算法
1、顺序查找(无序)
for循环遍历
2、二分查找(有序)
每次取中间值与要查找的数对比
代码:
const arr = [
0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 10, 11, 11, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 14, 15, 15, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 19, 20, 20, 20, 21, 22,
22, 22, 23, 23, 24, 25, 26, 26, 29, 31, 31, 33, 37, 37, 37, 38, 38, 43, 44, 44, 45, 48, 48, 49, 51, 52, 53, 53, 58,
59, 60, 61, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 68, 69, 70, 72, 72, 74, 75, 77, 77, 79, 79, 79, 83, 83, 84, 84, 86, 86, 86, 91, 92,
93, 93, 93, 94, 95, 96, 96, 97, 98, 100,
]
function search(num, arr){
let upperBound = arr.length - 1;
let lowerBound = 0;
while (upperBound >= lowerBound) {
let mid = Math.floor((upperBound + lowerBound) / 2);
if (arr[mid] < num) {
lowerBound = mid;
} else if (arr[mid] > num) {
upperBound = mid;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
console.log(search(5, arr));